PSM Publications
Canada doesn’t have track and trace
Canada doesn’t have track and trace January 2023 Download our factsheet about how Canadian importation breaks the U.S. track and trace system.
[...]Illegal Pill Presses Pose Serious, Nationwide Threat to American Patients and Communities
The Partnership for Safe Medicines and the National Association of Drug Diversion Investigators have released an update to 2019’s Illegal Pill Presses: An Overlooked Threat to American Patients.
Since the initial report, fentanyl deaths are higher than ever and these pills – created by clandestine pill presses around the globe – continue to be sold on the streets and on the dark web.
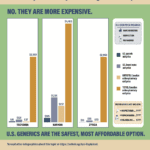
[...]Are safety-tested imported drugs still cheaper? No. They are more expensive.
Testing medicine for legitimacy is a complicated process. Across 24 different prescription medicines, the average cost to test a single dose is $2,750. However, ensuring that a batch of 100 pills is 90% certain to be safe requires testing at least 22 pills. Achieving 99.999% certainty requires even more testing, at tremendous expense. Once you’ve done the required testing, U.S. generics are cheaper. To learn more about this topic, read PSM’s summary: safedr.ug/Acri-Explained.
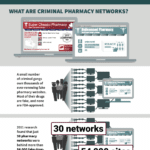
[...]Criminal Internet Pharmacy Networks Are Capitalizing on COVID-19.
In May 2020, the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP) released Rogue Online Pharmacies in the Time of Pandemic: Capitalizing on Misinformation and Fear, which focuses on how established fake pharmacy networks have pivoted to cash in on the coronavirus. PSM’s illustrated version of the report offers a compact summary of NABP’s work. Watch…
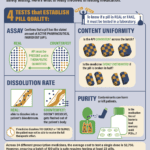
[...]How Many Tests Need to Be Performed to Know That a Batch of Pills is Safe?
Testing medicine for legitimacy is a complicated process. Across 24 different prescription medicines, the average cost to test a single dose is $2,750. However, ensuring that a batch of 100 pills is 90% certain to be safe requires testing at least 22 pills. Achieving 99.999% certainty requires even more testing, at tremendous expense. To learn more about this topic, read PSM’s summary: safedr.ug/Acri-Explained.
[...]Avoid COVID scams by buying medicine safely – Read our tips in English and en Español
Download our guide, AVOID SCAMS & COUNTERFEITS: Quick Tips to Safely Purchase Medicines Online (in English | en Español) to learn more about how to protect yourself and your loved ones from fake COVID-19 treatments.
[...]HHS comments come in overwhelmingly against Canadian drug importation proposal
Yesterday ended a 78-day comment period for the White House’s proposal to import medicine from Canada. In all, over 1,000 comments were filed. Overwhelmingly, these comments opposed the proposed rule or expressed skepticism that the rule could meet the two requirements listed in the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003: be safe and save consumers money. In fact, when you read the comments, it is clear that this policy is overwhelming opposed by experts on the issues of economics and medicine safety.
[...]Infographic: Counterfeiting By The Numbers
Our infographic, “Counterfeiting by the Numbers,” highlights facts from the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s January 2020 report, Combating Trafficking in Counterfeit and Pirated Goods, which documents the extraordinary scale of the global counterfeiting market and its effects across all economic sectors—including medicines.
[...]How do you test whether a medication is legitimate?
Testing medicine for legitimacy is a complicated process. Across 24 different prescription medicines, the average cost to test a single dose is $2,750. However, ensuring that a batch of 100 pills is safe requires testing at least 22 pills. To learn more about this topic, read PSM’s summary: safedr.ug/Acri-Explained.
[...]Myth: We are getting the same drugs Canadians take
In 2014, during a two-year period when Maine was experimenting with drug importation, the president of Maine’s Pharmacy Association purchased medications from an online pharmacy for testing. The drugs he received were not approved for the Canadian or U.S. markets. Worse, they were poor quality: two of them were the wrong strength, and the other was contaminated.
[...]